The advent of agentic AI—autonomous, goal-oriented agents capable of performing tasks without human intervention—marks a significant shift in artificial intelligence. These systems, often comprising specialized agents with distinct roles and expertise, offer unprecedented efficiency and scalability. However, this autonomy introduces complex data privacy challenges that organizations must address to ensure compliance and maintain user trust.
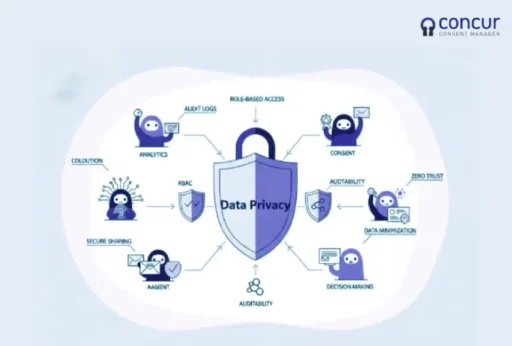
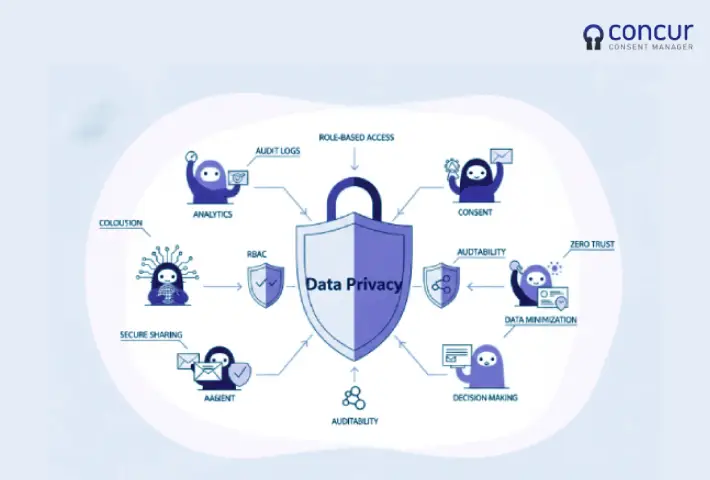
1. Role-Based Data Access
In agentic AI ecosystems, agents are designed to perform specific functions, such as data analysis, decision-making, or task automation. Each agent’s access to data should be strictly governed by its role and responsibilities. Implementing Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) ensures that agents access only the data necessary for their tasks, minimizing the risk of unauthorized data exposure.
Example: An agent responsible for financial analysis should not have access to personal user data unless explicitly required for its function.
2. Exposure to Different Large Language Models (LLMs)
Agents may interact with various LLMs, each with distinct capabilities and data handling practices. The exposure to different LLMs raises concerns about data leakage and inconsistent privacy standards. Organizations must establish clear guidelines on which LLMs agents can interact with and ensure that these models comply with the organization’s data privacy policies.
Recent Development: Anthropic’s decision to use user chats from its Claude chatbot for training its models, unless users opt out, highlights the importance of understanding how external models handle user data
3. Inter-Agent Data Sharing
Agents often collaborate by sharing data and insights to achieve common goals. While this collaboration enhances efficiency, it also increases the risk of data breaches if not properly managed. Implementing secure data-sharing protocols and ensuring that data is anonymized or encrypted during transmission can mitigate these risks.
Consideration: Establishing trust frameworks among agents can help ensure that data sharing adheres to predefined privacy standards
4. Auditability and Accountability
The autonomous nature of agentic AI complicates the tracking of data access and usage. Without proper audit trails, it becomes challenging to attribute actions to specific agents, hindering accountability. Organizations should implement robust logging mechanisms that record agent activities, data access events, and decision-making processes to facilitate audits and ensure compliance.
Challenge: The lack of clear traceability in agentic AI decision-making processes can weaken accountability and complicate efforts to achieve regulatory compliance
5. Data Minimization and Retention
Adhering to the principle of data minimization is crucial in agentic AI systems. Agents should collect and retain only the data necessary for their operations. Establishing clear data retention policies ensures that data is not stored longer than needed, reducing the risk of unauthorized access and potential breaches.
Guideline: Regularly review and purge unnecessary data to align with data protection regulations and minimize exposure
6. Security and Isolation
The interconnected nature of agents increases the potential attack surface. A breach in one agent can compromise the entire system. Implementing security measures such as sandboxing, encryption, and secure communication channels can isolate agents and protect sensitive data from unauthorized access.
Strategy: Adopting a Zero Trust Architecture, where every request is authenticated and authorized, can enhance security in agentic AI systems
7. Data Ownership and User Consent
Determining data ownership in agentic AI environments can be complex. Organizations must establish clear policies regarding data ownership and ensure that users provide informed consent for data collection and processing. Transparent communication about data usage can build trust and ensure compliance with data protection laws.
Example: Providing users with options to opt out of data collection or to delete their data upon request can empower users and demonstrate a commitment to privacy
As agentic AI continues to evolve, addressing data privacy challenges is paramount. By implementing role-based access controls, ensuring secure data sharing, maintaining auditability, adhering to data minimization principles, enhancing security, and clarifying data ownership, organizations can navigate the complexities of data privacy in autonomous AI systems. Proactively addressing these concerns will not only ensure compliance but also foster trust and confidence in the capabilities of agentic AI.