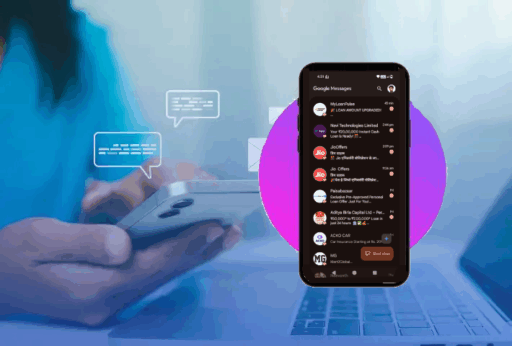
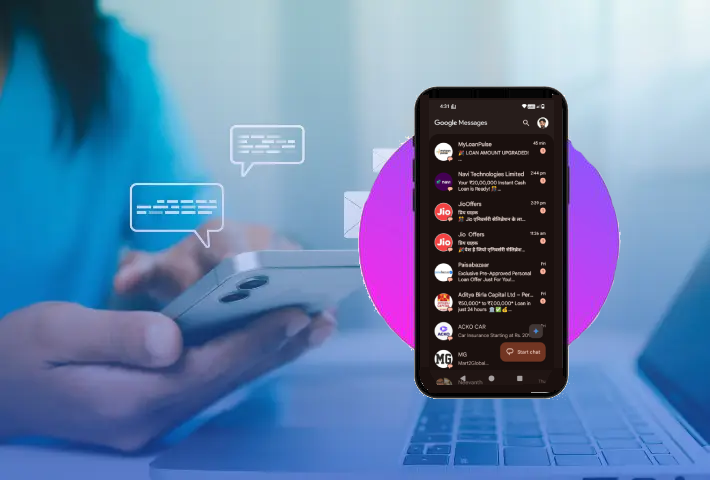
If you have checked your inbox in Android recently, you may have noticed messages that are not just plain text – images, GIF, and interactive buttons are now displaying in your texts! Enter RCS, or Rich Communication Services. SMS on steroids – read receipts, typing indicators, as well as rich media, all in one smooth experience. RCS, in India, has started to gain traction with applications like Google Messages, offering a more dynamic and interactive way for us to connect – however a new host of issues arise with every revolution of services that users will want to be aware of.
RCS does offer some advantages over SMS. SMS uses the cell phone network that uses an SMSC to pass messages based on our phone number.RCS uses the internet. Therefore, messages are sent over mobile data or wi-fi. It has the potential to offer a richer communication experience. For example, images will display in high resolution. Videos can be streamed. We can have interactive buttons and even typing indicators in real time. Compared to SMS, RCS does not need to rely only on the telecom carrier’s infrastructure. RCS can reach the user much faster. It can offer larger message sizes. It can also provide a seamless experience across devices and applications. This makes it much closer to using chat applications in contrast to the SMS inbox.
What is RCS Messaging?
Rich Communication Services (RCS) is a modern messaging protocol. It is built to upgrade and eventually replace traditional SMS and MMS. Unlike SMS, which is restricted to plain text, it relies on telecom carrier infrastructure. RCS uses the internet through mobile data or Wi-Fi. It delivers far more advanced features. With RCS, users can exchange high-resolution images and videos. They can see when the other person is typing or has read a message. They can enjoy enhanced group chats and even interact with businesses through rich buttons and quick replies.
The Emergence of RCS Spam
Initially, RCS was seen as a possible solution to SMS spam, as it potentially offered users a cleaner messaging experience in a more secure environment. However, businesses soon saw its use potential and RCS quickly became a new format for unrequested advertising. From flashy ads that users received by mistake like a few personal loan offers, the users were receiving unwanted RCS-based ads, even on devices without an installed SIM card. The flood of spam led Google to take some action. In June 2022, the company paused RCS Business Messaging in India, in an effort to stop misuse and behalf of user protection to limits sources of intruding communications but its active again.
DPDPA 2023 and RCS Messaging: Data Privacy and Compliance Rules
The Digital Personal Data Protection Act (DPDPA) 2023, enacted in August 2023. The DPDPA aims to regulate the processing of personal data and establish a Data Protection Board to handle grievances. RCS system needs to be considered as it’s beyond under currently SMS infrastructure in India which has a DLT system acting as an identifier for commercial, promotional and other message.
Organizations must obtain explicit consent to process personal data under DPDPA. With the rise of RCS spam, the legality and compliance with required consent will need to be considered seriously. Organizations engaged in unsolicited RCS may be liable for non-compliance and possibly face fines.
How TRAI and Regulators Are Tackling RCS Spam in India
TRAI has taken steps to limit spam by developing suffix-based classifications for SMS messages (Promotional, S for Service-related, and T for Transactional and G for Government-initiated). The idea is designed to promote transparency and allow users to identify the nature of the messages they are receiving.
Even with regulatory responses, challenges remain to stem RCS spam. Telecom operators want stricter guidelines to limit unsolicited communications using business messaging formats. The fast-moving nature of digital communications will require constant regulatory adaptation.
Checklist for Businesses and Safety Guide for Users
For Businesses:
- Explicit Consent Collection: Businesses must obtain a clear referenced consent from recipients before sending out RCS messaging, and DPDPA mandates that you only process personal data lawfully.
- Show Rigorous Reporting and Blocking Systems: Install systems to allow users to report unsolicited messages and block senders thereby maintaining compliance and trust.
- Safeguard Against Misuse: Communication platforms must be designed in such a way as to prevent scams, phishing or other cybercrime. While the telecoms equip the infrastructure, it is a fluke if the company ensues their messaging does not continue to contribute to fraudulent behaviour or violate data privacy principles.
For Users:
- Stay Informed: Continue to keep up with new regulatory changes like DPDPA 2023 provisions, so you can become informed about your rights over your personal data and digital communications.
- Leverage DPDPA Notice: Utilize the DPDPA notice and provide consent ONLY for when RCS communications will be acceptable.
- Report Suspicious Activity: Report possible spam, scammers, or suspicious RCS messages to legal authorities or to your service provider to improve enforcement and reduce abuser’s acts.
Transitioning from SMS to RCS represents a major step forward in the normal evolution of digital communications. However, RCS introduces improved functionality alongside challenges regarding data privacy and spam. As we collectively develop these policies, it is important to look beyond and continue working with regulators, businesses, and users.
RCS represents a hybrid landscape. Messaging is internet based, but we are still subject to the telecom and data protection obligations. So, regulators, businesses, and users need to come together in a collaborative process; business should provide privacy by design, regulators should require consent and transparency standards, and users need to be proactive. Together, this framework means that RCS messaging can remain a secure, compliant, and trusted channel for communication.